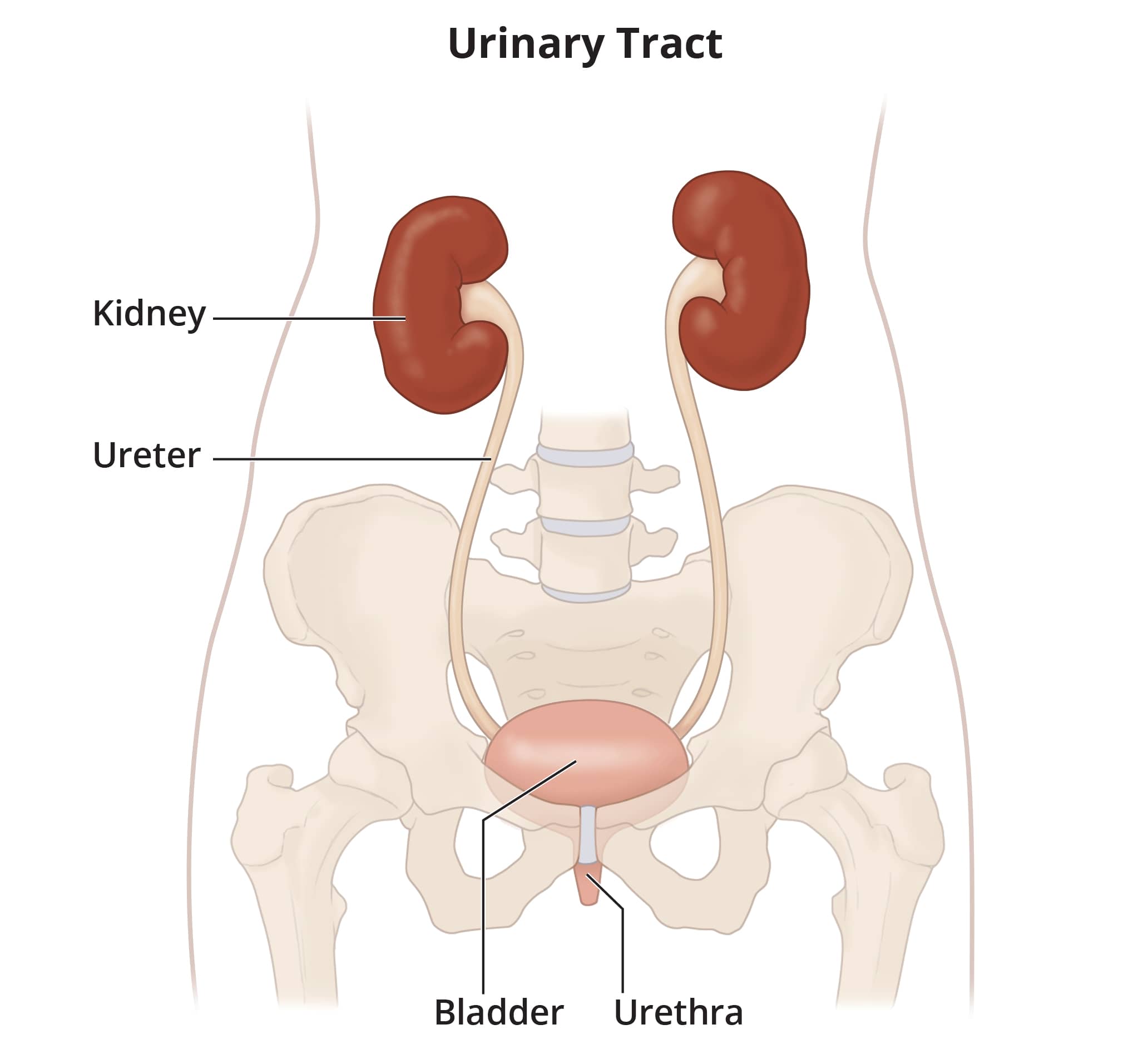
What is an urinary tract ?
A urinary tract surgery is a surgery in any part of your urinary system — your kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most surgeries involve the lower urinary tract — the bladder and the urethra.
Women are at greater risk of developing a Urinary tract infection UTI than men. Infection limited to your bladder can be painful and annoying. However, serious consequences can occur if a Urinary tract infection UTI spreads to your kidneys.
Doctors typically treat urinary tract infections with antibiotics. But you can take steps to reduce your chances of getting a Urinary tract infection UTI in the first place.
Symptoms
Urinary tract infections don’t always cause signs and symptoms, but when they do they may include:
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate
- A burning sensation when urinating
- Passing frequent, small amounts of urine
- Urine that appears cloudy
- Urine that appears red, bright pink or cola-colored — a sign of blood in the urine
- Strong-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain, in women — especially in the center of the pelvis and around the area of the pubic bone
Risks and Side Effects
Urinary tract infections are common in women, and many women experience more than one infection during their lifetimes
- Female anatomy. A woman has a shorter urethra than a man does, which shortens the distance that bacteria must travel to reach the bladder.
- Sexual activity. Sexually active women tend to have more UTIs than do women who aren’t sexually active. Having a new sexual partner also increases your risk.
- Certain types of birth control. Women who use diaphragms for birth control may be at higher risk, as well as women who use spermicidal agents.
- Menopause. After menopause, a decline in circulating estrogen causes changes in the urinary tract that make you more vulnerable to infection.
